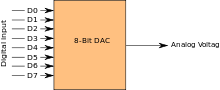
首先得说,模数转换器(ADC)和数模转换器(DAC)是连接模拟世界和数字世界的桥梁,对于信号的数字化革命起到了巨大的作用。
其中的数模转换器,英文有多种说法,主要的有DAC,D/A,D-A, D2A, D-to-A,它是将数字信号(一般为二进制)转换为模拟量(电流、电压或电荷)的一种功能。模数转换器(ADC)则正好相仿。与模拟信号不同的是,数字信号即便经过很复杂的系统也可以无损耗低进行传输、处理以及存储。
DAC有几种不同的架构,根据应用可以通过以下的6个主要参量选择相应的结构:
- 物理大小
- 功耗
- 分辨率
- 转换速度
- 准确度
- 成本
DAC最先被广泛用在音乐播放器中,将数字信号流转换为模拟音频信号,后期也广泛应用在数字电视、手机中。在数字音频中使用的是低速、高分辨率类型的DAC,而在数字视频中则使用高速、中低分辨率的DAC。在军用雷达系统中一般使用分离的DAC,这种DAC的速度非常高、分辨率较低、功耗较高。高速的测试测量仪器,尤其是取样示波器中使用的也基本都是这种分离的高速、低分辨率数模转换器(DAC)。
概述
数模转换器是将一个抽象的有限精确的数字(通常为定点二进制数)转换为一个物理量(比如电压或压力)更多地是将有限精确的时间序列数字转换为一个连续变化的物理信号。 一个理想的DAC An ideal DAC converts the abstract numbers into a conceptual sequence of impulses that are then processed by a reconstruction filter using some form of interpolation to fill in data between the impulses. A typical practical DAC converts the numbers into a piecewise constant function made up of a sequence of rectangular functions that is modeled with the zero-order hold. Other DAC methods (e.g., methods based on delta-sigma modulation) produce a pulse-density modulated signal that can then be filtered in a similar way to produce a smoothly varying signal.
As per the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, a DAC can reconstruct the original signal from the sampled data provided that its bandwidth meets certain requirements (e.g., a baseband signal with bandwidth less than the Nyquist frequency). Digital sampling introduces quantization error that manifests as low-level noise added to the reconstructed signal.
实际的工作
 实际的应用中,需要在DAC的输出端加入一个滤波器或有限带宽的器件将DAC输出的台阶响应平滑为连续的曲线。将时间上分离的点通过类似内插机制的平滑重构得到连续变化的信号电平。
实际的应用中,需要在DAC的输出端加入一个滤波器或有限带宽的器件将DAC输出的台阶响应平滑为连续的曲线。将时间上分离的点通过类似内插机制的平滑重构得到连续变化的信号电平。
These numbers are written to the DAC, typically with a clock signal that causes each number to be latched in sequence, at which time the DAC output voltage changes rapidly from the previous value to the value represented by the currently latched number. The effect of this is that the output voltage is held in time at the current value until the next input number is latched, resulting in a piecewise constant or staircase-shaped output. This is equivalent to a zero-order hold operation and has an effect on the frequency response of the reconstructed signal.
The fact that DACs output a sequence of piecewise constant values (known as zero-order hold in sample data textbooks) or rectangular pulses causes multiple harmonics above the Nyquist frequency. Usually, these are removed with a low pass filter acting as a reconstruction filter in applications that require it.
应用
DAC类型
最常见的类型:
- 脉宽调制型,也是最简单的DAC类型。 在一个低通模拟滤波器上以开关的方式施加一个稳定的电流货电压信号,开关切换的持续时间取决于数字输入量。这种方式常被用在电机马达的控制以及其它很多应用中。
- 过取样DAC,又叫内插DAC,例如delta-sigma DAC采用了脉冲密度转换技术. 这种技术允许使用比较低分辨率的DAC,比较常用的是1-bit DAC
- The binary-weighted DAC, which contains individual electrical components for each bit of the DAC connected to a summing point. These precise voltages or currents sum to the correct output value. This is one of the fastest conversion methods but suffers from poor accuracy because of the high precision required for each individual voltage or current. Such high-precision components are expensive, so this type of converter is usually limited to 8-bit resolution or less.[citation needed]
- 开关电阻DAC包含了一个并行的电阻网络。 contains a parallel resistor network. Individual resistors are enabled or bypassed in the network based on the digital input.
- 开关电容源DAC, from which different current sources are selected based on the digital input.
- 开关电容DAC包含了一个并行的电容网络. Individual capacitors are connected or disconnected with switches based on the input.
- The R-2R ladder DAC which is a binary-weighted DAC that uses a repeating cascaded structure of resistor values R and 2R. This improves the precision due to the relative ease of producing equal valued-matched resistors (or current sources).
- The Successive-Approximation or Cyclic DAC, which successively constructs the output during each cycle. Individual bits of the digital input are processed each cycle until the entire input is accounted for.
- The thermometer-coded DAC, which contains an equal resistor or current-source segment for each possible value of DAC output. An 8-bit thermometer DAC would have 255 segments, and a 16-bit thermometer DAC would have 65,535 segments. This is perhaps the fastest and highest precision DAC architecture but at the expense of high cost. Conversion speeds of >1 billion samples per second have been reached with this type of DAC.
- Hybrid DACs, which use a combination of the above techniques in a single converter. Most DAC integrated circuits are of this type due to the difficulty of getting low cost, high speed and high precision in one device.
- The segmented DAC, which combines the thermometer-coded principle for the most significant bits and the binary-weighted principle for the least significant bits. In this way, a compromise is obtained between precision (by the use of the thermometer-coded principle) and number of resistors or current sources (by the use of the binary-weighted principle). The full binary-weighted design means 0% segmentation, the full thermometer-coded design means 100% segmentation.
- Most DACs, shown earlier in this list, rely on a constant reference voltage to create their output value. Alternatively, a multiplying DAC[1] takes a variable input voltage for their conversion. This puts additional design constraints on the bandwidth of the conversion circuit.
DAC性能
DACs are very important to system performance. The most important characteristics of these devices are:
- 分辨率: The number of possible output levels the DAC is designed to reproduce. This is usually stated as the number of bits it uses, which is the base two logarithm of the number of levels. For instance a 1 bit DAC is designed to reproduce 2 (21) levels while an 8 bit DAC is designed for 256 (28) levels. Resolution is related to the effective number of bits which is a measurement of the actual resolution attained by the DAC. Resolution determines color depth in video applications and audio bit depth in audio applications.
- 最高采样率: A measurement of the maximum speed at which the DACs circuitry can operate and still produce the correct output. As stated above, the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem defines a relationship between this and the bandwidth of the sampled signal.
- 单调性: The ability of a DAC's analog output to move only in the direction that the digital input moves (i.e., if the input increases, the output doesn't dip before asserting the correct output.) This characteristic is very important for DACs used as a low frequency signal source or as a digitally programmable trim element.
- 总谐波失真和噪声(THD+N): A measurement of the distortion and noise introduced to the signal by the DAC. It is expressed as a percentage of the total power of unwanted harmonic distortion and noise that accompany the desired signal. This is a very important DAC characteristic for dynamic and small signal DAC applications.
- 动态范围: A measurement of the difference between the largest and smallest signals the DAC can reproduce expressed in decibels. This is usually related to resolution and noise floor.
Other measurements, such as phase distortion and jitter, can also be very important for some applications, some of which (e.g. wireless data transmission, composite video) may even rely on accurate production of phase-adjusted signals.
Linear PCM audio sampling usually works on the basis of each bit of resolution being equivalent to 6 decibels of amplitude (a 2x increase in volume or precision).
Non-linear PCM encodings (A-law / μ-law, ADPCM, NICAM) attempt to improve their effective dynamic ranges by a variety of methods - logarithmic step sizes between the output signal strengths represented by each data bit (trading greater quantisation distortion of loud signals for better performance of quiet signals)
DAC品质因素
- 静态性能:
- 差分非线性(DNL) shows how much two adjacent code analog values deviate from the ideal 1 LSB step.[2]
- 积分非线性(INL) shows how much the DAC transfer characteristic deviates from an ideal one. That is, the ideal characteristic is usually a straight line; INL shows how much the actual voltage at a given code value differs from that line, in LSBs (1 LSB steps).
- 增益
- 偏移
- 噪声 is ultimately limited by the thermal noise generated by passive components such as resistors. For audio applications and in room temperatures, such noise is usually a little less than 1 μV (microvolt) of white noise. This limits performance to less than 20~21 bits even in 24-bit DACs.
- 频域性能
- 无杂散动态范围(SFDR) indicates in dB the ratio between the powers of the converted main signal and the greatest undesired spur.
- 信号噪声/失真比率(SNDR) indicates in dB the ratio between the powers of the converted main signal and the sum of the noise and the generated harmonic spurs
- i-th谐波失真(HDi) indicates the power of the i-th harmonic of the converted main signal
- 总谐波失真(THD) is the sum of the powers of all HDi
- If the maximum DNL error is less than 1 LSB, then the D/A converter is guaranteed to be monotonic. However, many monotonic converters may have a maximum DNL greater than 1 LSB.
- 时域性能:
- 毛刺脉冲区域(毛刺能量)
- 响应非确定性
- 时间非线性(TNL)