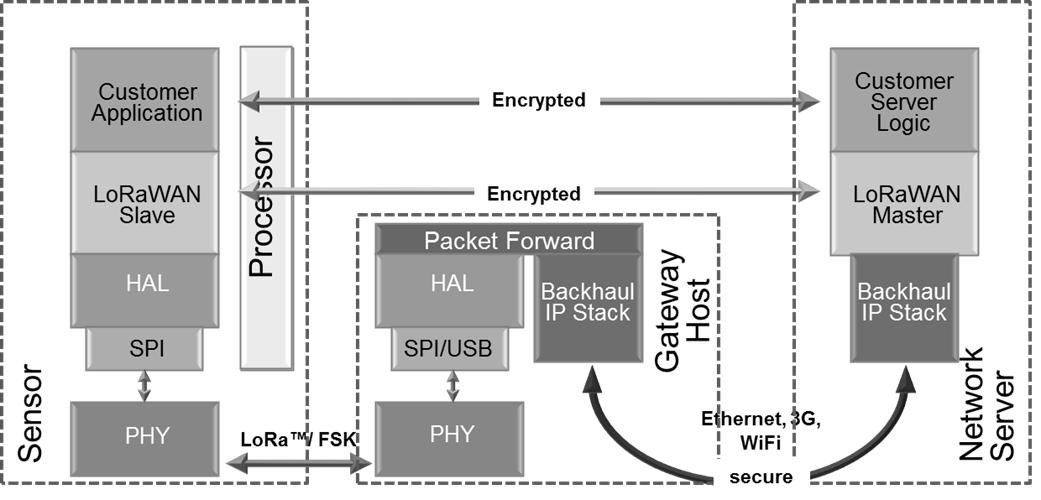
LoRa是长距离(Long Range)的缩写,作为低功耗广域网(LPWAN)中的一种无线技术,相对于其他无线技术(如Sigfox、NB-IOT等),LoRa产业链较为成熟、商业化应用较早。
LoRa无线技术的主要特点
长距离:1 ~ 20 km
节点数:万级,甚至百万级
电池寿命:3~10年
数据速率0.3~50kbps
LoRa应用
从目前的LoRa应用情况来看,主要有数据透传和LoRaWAN协议应用。目前还是用LoRa作为数据透传的多,由于网关技术和开发的门槛比较高,使用LoRaWAN协议组网的应用还是比较少。
LoRa应用需要考虑的几个问题
距离或范围
供电或功耗
节点数
应用场景
成本
LoRa作为一种无线技术,基于Sub-GHz的频段使其更易以较低功耗远距离通信,可以使用电池供电或者其他能量收集的方式供电。较低的数据速率也延长了电池寿命和增加了网络的容量。LoRa信号对建筑的穿透力也很强。LoRa的这些技术特点更适合于低成本大规模的物联网部署。 在城市里,一般无线距离范围在1~2公里,郊区或空旷地区,无线距离会更远些。网络部署拓扑布局可以根据具体应用和和场景设计部署方案。LoRa适合于通信频次低,数据量不大应用。一个网关可以连接多少个节点或终端设备,按照Semtech官方的解释:一个SX1301有8个通道,使用LoRaWAN协议每天可以接受约150万包数据。如果你的应用每小时发送一个包,那么一个SX1301网关可以处理大约62500个终端设备。 从LoRa网络应用方面看,有大网和小网之分。小网是指用户自设节点、网关和服务器,自成一个系统网络;大网就是大范围基础性的网络部署,就像中国移动的通信网络一样。从LoRa行业从业者来看,有不少电信运营商也参与其中。随着LoRa设备和网络的增多,相互之间的频谱干扰是存在的,这就对通信频谱的分配和管理提出了要求,需要一个统一协调管理的机制,一个大网的管理。
LoRa RF信息
The LoRa RF or physical layer encapsulates the all the direct contact with the outside world over the radio interface.
The RF parameters including frequencies, bands, power levels, modulation, and the basic RF protocols are all encapsulated in the LoRa RF or physical layer attributes. LoRa frequency bands
The LoRa wireless system makes use of the unlicensed frequencies that are available worldwide. The most widely used frequencies / bands are:
868 MHz for Europe 915 MHz for North America 433 MHz band for Asia
Using lower frequencies than those of the 2.4 or 5.8 GHz ISM bands enables much better coverage to be achieved especially when the nodes are within buildings.
Although the sub-1GHz ISM bands are normally used, the technology is essentially frequency agnostic and can be used on most frequencies without fundamental adjustment. LoRa modulation
LoRa RF physical layer uses a form of spread spectrum modulation. The LoRa modulation scheme uses wide-band linear frequency modulated pulses. The level of frequency increase or decrease over time is used to encode the data to be transmitted, i.e. a form of chirp modulation.
This form of modulation enables LoRa systems to demodulate signals that are 20dB below the noise floor when the demodulation is combined with forward error correction, FEC. This means that the link budget for a LoRa system can provide an improvement of more than 25dB when compared to a traditional FSK system. LoRa adaptive link
The fact that only low data rates are used, and low levels of overall data transfer means that low bandwidths are required. A variety of bandwidths are available: 7.8 kHz; 10.4 kHz; 15.6 kHz; 20.8 kHz; 31.2 kHz; 41.7 kHz; 62.5 kHz; 125 kHz; 250 kHz; 500 kHz. The required bandwidth can be selected according to the data requirements as well as the link conditions.
The power level used within LoRa RF physical layer is adaptive. The power level used is dependent upon the data rate needed, link conditions etc. An algorithm is used to determine the required power level - the transmitted power is normally backed off a little from the maximum needed to support fast communications and in this way the battery life is maximised and network capacity maintained. LoRa data communications
The communication between different end-devices and gateways utilises several different frequency channels and it uses different data rates.
The choice of the data rate is a balance between communication range and message duration, i.e. the rate at which the required data can be sent.
The use of the chirp spread spectrum technology enables communications with different data rates not interfere with each other. In this way a set of “virtual” channels is created which increases the capacity of the gateway.